Enamel Hypoplasia. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation. Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). The condition results in thin enamel. These disturbances are defects in enamel development.
Plane Form Enamel Hypoplasia Wikipedia
Enamel Hypoplasia Smiles For Kids. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). The condition results in thin enamel. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. These disturbances are defects in enamel development. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth.
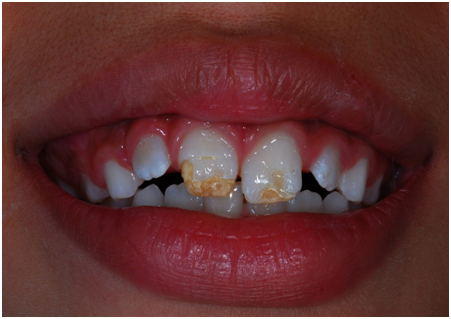
The enamel that the teeth do have is usually hard and healthy, but there is not enough of it to fully protect the teeth.
Disturbance that takes place during formation of the enamel matrix what are the systemic etiological factors that are related to hypoplasia and hypocalcification? Enamel is the hardest tissue of body and marks of enamel hypoplasia (eh) remain unaltered even during. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition where the outer layer of a tooth fails to develop properly, this may put your pet's teeth at risk for infection or fracture. When deeper lesions are seen as small grooves or pits is. These disturbances are defects in enamel development. Usually the condition involves part of the tooth having a pit in it. Enamel hypoplasia is common in children with low birthweight or systemic illness in the neonatal •enamel hypoplasia (or 4.2) •presence of s. More questions pertaining enamel hypoplasia can be answered by the experts on justanswer. Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. Dental enamel hypoplasia, a defect of enamel formation, has been widely used for the investigation of growth disruptions in past. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount, caused by defective enamel matrix formation with a deficiency of vitamin d in the body. It is sometimes identified as a physically missing tooth structure. What are enamel hypoplasia treatments? Enamel hypoplasia may be inherited, or result from illness, malnutrition, trauma, or high. This condition is known as enamel hypoplasia. Enamel hypoplasia (eh) is a developmental defect that can affect the primary and permanent teeth in one of two ways. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). Disturbance that takes place during formation of the enamel matrix what are the systemic etiological factors that are related to hypoplasia and hypocalcification? What does enamel hypoplasia mean? Read more about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications, causes and. Cathy explains that enamel hypoplasia is when a tooth has less enamel than is normal. 1 department of oral medicine and radiology guided by 7. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. What is the definition of enamel hypoplasia? Enamel hypoplasia is a defect that affects the way the teeth develop, causing them to have poor enamel matrix formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by a disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. Meaning of enamel hypoplasia medical term.
Enamel Hypoplasia Wikipedia
Enamel Hypoplasia Brilliant Dentist Society. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. These disturbances are defects in enamel development. Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. The condition results in thin enamel.
Management Of Acquired Enamel Hypoplasia Involving The Incisors And Molars A Case Report Jpda
Enamel Hypoplasia Of The Left Maxillary Incisors In A Child Intubated Download Scientific Diagram. The condition results in thin enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. These disturbances are defects in enamel development. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation.
Clinical Decision Making For Diagnosis And Treatment Of Dental Enamel Injuries
Science Source Enamel Hypoplasia. Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth. These disturbances are defects in enamel development. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. The condition results in thin enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired.
Amelogenesis Imperfecta Wikipedia
Enamel Hypoplasia Archives Soap Goddess. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired. Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). These disturbances are defects in enamel development. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. The condition results in thin enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing.
Enamel Hypoplasia Veterinary Dental Center Thin Enamel Wall
Enamel Hypoplasia Bomstad Dental. Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired. Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth. The condition results in thin enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. These disturbances are defects in enamel development.
Prevalence Of Dental Enamel Defects In Children And Adolescents From Pasto Colombia
What Is Enamel Hypoplasia. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. These disturbances are defects in enamel development. Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. The condition results in thin enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel.
Enamel Hypoplasia Brilliant Dentist Society
What Are The Treatments For Enamel Hypoplasia With Pictures. Still, it can affect both baby teeth and permanent teeth. Some medications can also affect the teeth that were developing at the time of dosage. Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. View enamel hypoplasia research papers on academia.edu for free. Enamel hypoplasia is typically caused by malnutrition, illness, infection or fever during tooth formation. Enamel hypoplasia causes enamel hypoplasia treatment enamel hypoplasia prevention. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount,1 caused by defective enamel matrix formation. The condition results in thin enamel. Enamel defects can be congenital or acquired. Enamel hypoplasia is a condition characterized by transverse lines, pits, and grooves on the surface of tooth crowns. Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the enamel that only occurs while teeth are still developing. Enamel hypoplasia (also known as turner's tooth, or turner's hypoplasia) is a condition most commonly observed in permanent bicuspid teeth (secondary to infected primary molars). Enamel hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. These disturbances are defects in enamel development. Enamel hypoplasia is a surface defect of the tooth crown caused by disturbance of enamel matrix secretion.